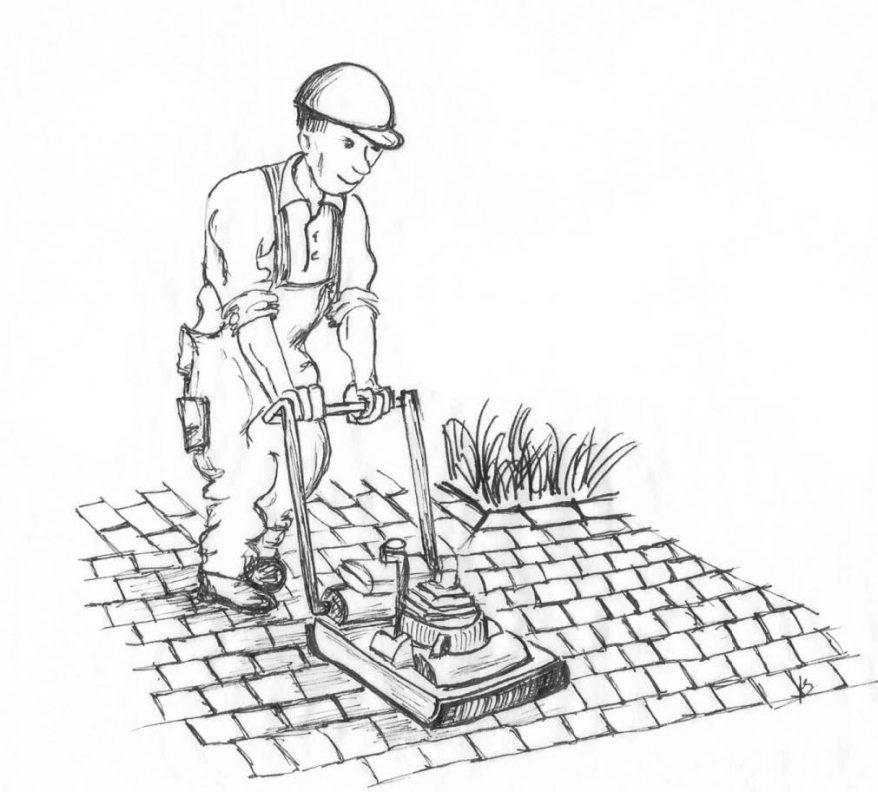
STAGE I - EXCAVATING SO-CALLED TRENCHING
The process of trenching consists of removing the top layer of the native substrate from 20-40 cm depth. If you have a small area, you can easily do it yourself. And if you do a large area, you must do it with road machines such as dozers, compactors, and crushers, which will significantly accelerate the progress of the job.
STAGE II – ALIGNMENT AND LEVELING OF BASIS
After the completion of the trenching, the compensation and the completion of the target slopes and drainage lines shall be ensured that each of the substructure layers has the same thickness in each area of the planned site. This action is known as ground leveling. It can also be done manually with a patch and a precision level, and on larger surfaces with a leveling instrument and road machines. This involves filling the holes and removing the excess ground according to the predefined elevation rows. During this phase, junctions and turnouts are being determined, but above all the shape of the road and roadside levels. Ground leveling is of key importance. Particular precision is recommended due to the future appearance of the surface and its durability.
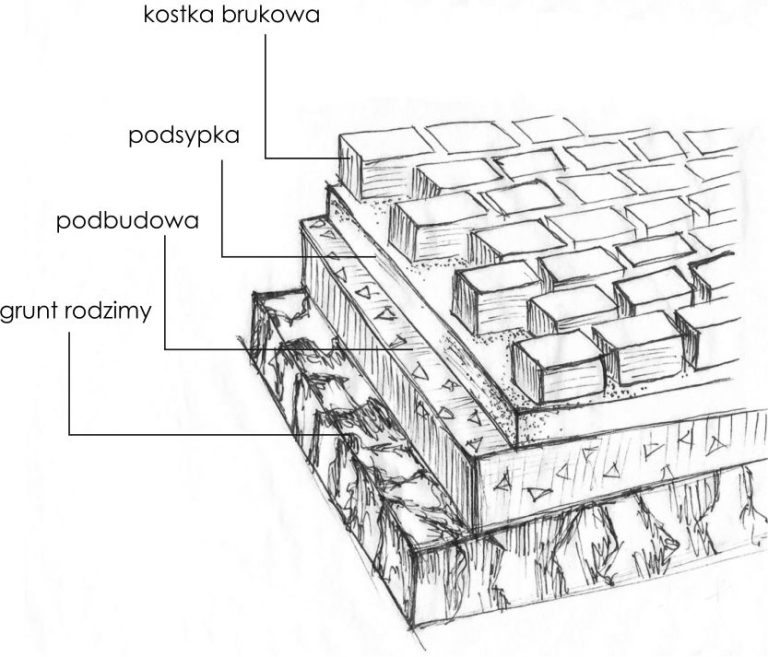
STAGE III - SUBSTRUCTURE
A well-prepared substructure is the most important issue for the durability of the surface. It gives the upper layer a good stiffness and the distribution of forces during use. The structure of the substructure is influenced by several factors:
- the type of native ground
- size and type of load
- groundwater status
- method of drainage
In contrast, the thickness of the substructure is directly affected by the type of support and the anticipated loads to be applied to the site. In this way, paving around the house, e.g., sidewalks, will be less thick (about 20 cm) than a layer designed for vehicle traffic (about 30 cm).
The material used for the construction of the sub-structure is determined by the intensity of the loads and the ground conditions. The most common material is natural or broken aggregates, used for low loads. As they are intensified, this raw material is replaced by lean concrete or crushed stone. The substructure process itself can be divided into several stages depending on the thickness of the layer. This results in uniform compaction of the entire layer. Aggregate or other road paving material is decomposed and compacted to the recommended density. The substructure of lean concrete is carried out similarly to that of aggregates. Use low water content concrete.
STAGE IV - SUBBASE
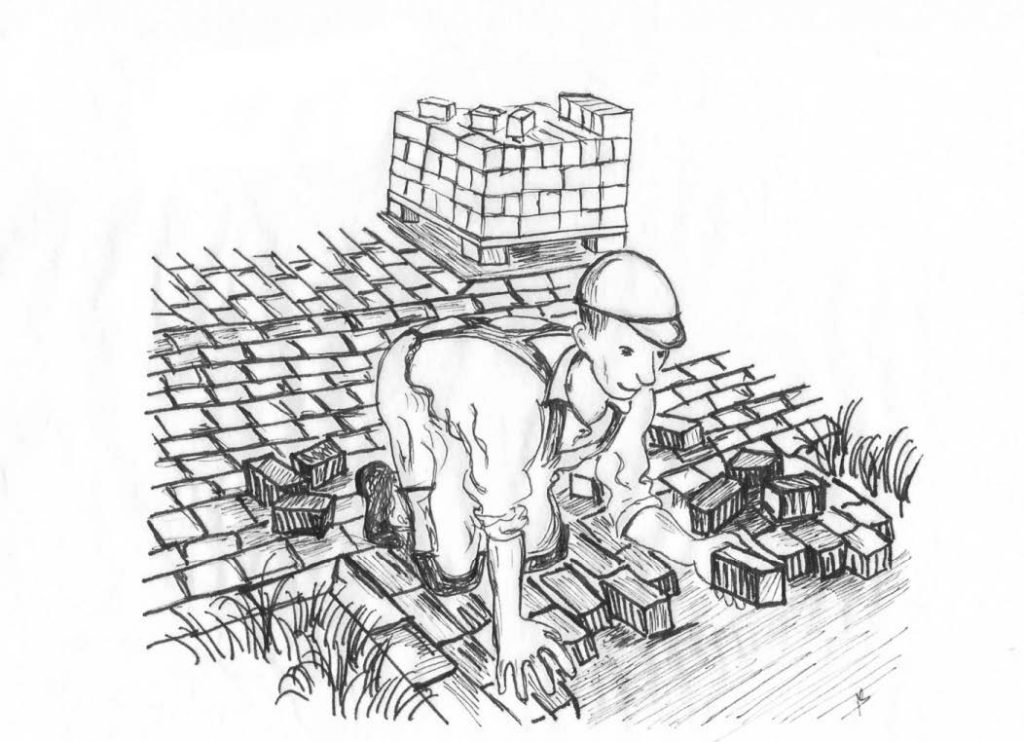

STEP V - LAYING OF PAVING STONES

